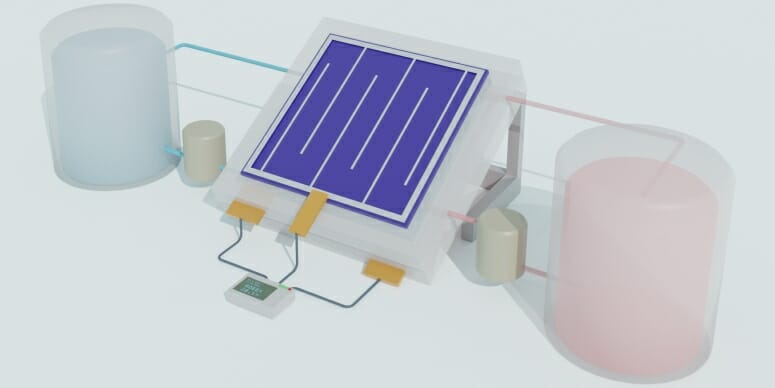
Schematic illustration of an integrated solar flow battery. A solar cell is hooked up to tanks of chemicals that can store electricity for later use. WENJIE LI
Chemists at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and their collaborators have created a highly efficient and long-lasting solar flow battery, a way to generate, store and redeliver renewable electricity from the sun in one device.
The new device is made of silicon solar cells combined with advanced solar materials integrated with optimally designed chemical components. The solar flow battery, made by the Song Jin lab in the UW–Madison chemistry department, achieved a new record efficiency of 20 percent. That bests most commercially available silicon solar cells used today and is 40 percent more efficient than the previous record holder for solar flow batteries, also developed by the Jin lab.
While solar flow batteries are years away from commercialization, they offer the potential to provide reliable electricity generation and storage for lighting, cell phones or other fundamental uses for homes in remote areas. They combine the advantages of photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity with the advantages of flow batteries, which use tanks of chemicals that can react to produce electricity and be recharged by the solar cells.
The researchers published their work July 13 in the journal Nature Materials. UW–Madison graduate student Wenjie Li is the lead author of the study. The Jin lab collaborated with researchers from the University of New South Wales and the University of Sydney in Australia, Utah State University, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi Arabia and the City University of Hong Kong.
Since the sun doesn’t always shine, storage is key for practical solar electricity, especially in remote and rural regions with a lot of sunlight, such as in the sunbelt regions of the U.S., Australia, Saudi Arabia and Africa. Many solar home systems use lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries for electricity storage. Flow batteries, which use large tanks of liquid chemicals to store energy, could be less expensive at a larger scale and are an ideal storage choice for merging with solar cells.
